 |
| August 16, 2016 | Volume 12 Issue 31 |
Mechanical News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite
 OPEN MIND Technologies has introduced its latest hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite, which includes a range of powerful enhancements to its core toolpath capabilities, as well as new functionality for increased NC programming efficiency in applications ranging from 2.5D machining to 5-axis milling. New and enhanced capabilities include: Optimized Deep Hole Drilling, a new algorithm for 3- and 5-axis Rest Machining, an enhanced path layout for the 3D Plane Machining cycle, better error detection, and much more.
OPEN MIND Technologies has introduced its latest hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite, which includes a range of powerful enhancements to its core toolpath capabilities, as well as new functionality for increased NC programming efficiency in applications ranging from 2.5D machining to 5-axis milling. New and enhanced capabilities include: Optimized Deep Hole Drilling, a new algorithm for 3- and 5-axis Rest Machining, an enhanced path layout for the 3D Plane Machining cycle, better error detection, and much more.
Learn more.
One-part epoxy changes from red to clear under UV
 Master Bond UV15RCL is a low-viscosity, cationic-type UV-curing system with a special color-changing feature. The red material changes to clear once exposed to UV light, indicating that there is UV light access across the adhesive material. Although this change in color from red to clear does not indicate a full cure, it does confirm that the UV light has reached the polymer. This epoxy is an excellent electrical insulator. UV15RCL adheres well to metals, glass, ceramics, and many plastics, including acrylics and polycarbonates.
Master Bond UV15RCL is a low-viscosity, cationic-type UV-curing system with a special color-changing feature. The red material changes to clear once exposed to UV light, indicating that there is UV light access across the adhesive material. Although this change in color from red to clear does not indicate a full cure, it does confirm that the UV light has reached the polymer. This epoxy is an excellent electrical insulator. UV15RCL adheres well to metals, glass, ceramics, and many plastics, including acrylics and polycarbonates.
Learn more.
SPIROL Press-N-Lok™ Pin for plastic housings
 The Press-N-Lok™ Pin was designed to permanently retain two plastic components to each other. As the pin is inserted, the plastic backfills into the area around the two opposing barbs, resulting in maximum retention. Assembly time is quicker, and it requires lower assembly equipment costs compared to screws and adhesives -- just Press-N-Lok™!
The Press-N-Lok™ Pin was designed to permanently retain two plastic components to each other. As the pin is inserted, the plastic backfills into the area around the two opposing barbs, resulting in maximum retention. Assembly time is quicker, and it requires lower assembly equipment costs compared to screws and adhesives -- just Press-N-Lok™!
Learn more about the new Press-N-Lok™ Pin.
Why hybrid bearings are becoming the new industry standard
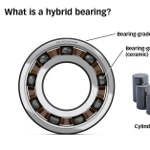 A combination of steel outer and inner rings with ceramic balls or rollers is giving hybrid bearings unique properties, making them suitable for use in a wide range of modern applications. SKF hybrid bearings make use of silicon nitride (twice as hard as bearing steel) rolling elements and are available as ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and in custom designs. From electric erosion prevention to friction reduction and extended maintenance intervals, learn all about next-gen hybrid bearings.
A combination of steel outer and inner rings with ceramic balls or rollers is giving hybrid bearings unique properties, making them suitable for use in a wide range of modern applications. SKF hybrid bearings make use of silicon nitride (twice as hard as bearing steel) rolling elements and are available as ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and in custom designs. From electric erosion prevention to friction reduction and extended maintenance intervals, learn all about next-gen hybrid bearings.
Read the SKF technical article.
3M and Ansys train engineers on simulating adhesives
 Ansys and 3M have created an advanced simulation training program enabling engineers to enhance the design and sustainability of their products when using tapes and adhesives as part of the design. Simulation enables engineers to validate engineering decisions when analyzing advanced polymeric materials -- especially when bonding components made of different materials. Understand the behavior of adhesives under real-world conditions for accurate modeling and design.
Ansys and 3M have created an advanced simulation training program enabling engineers to enhance the design and sustainability of their products when using tapes and adhesives as part of the design. Simulation enables engineers to validate engineering decisions when analyzing advanced polymeric materials -- especially when bonding components made of different materials. Understand the behavior of adhesives under real-world conditions for accurate modeling and design.
Read this informative Ansys blog.
New FATH T-slotted rail components in black from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added a wide assortment of black-colored FATH T-slotted hardware components to match their SureFrame black anodized T-slotted rails, including: cube connectors (2D and 3D) and angle connectors, joining plates of many types, brackets, and pivot joints. Also included are foot consoles, linear bearings in silver and black, cam lever brakes, and L-handle brakes. FATH T-slotted hardware components are easy to install, allow for numerous T-slotted structure configurations, and have a 1-year warranty against defects.
Automation-Direct has added a wide assortment of black-colored FATH T-slotted hardware components to match their SureFrame black anodized T-slotted rails, including: cube connectors (2D and 3D) and angle connectors, joining plates of many types, brackets, and pivot joints. Also included are foot consoles, linear bearings in silver and black, cam lever brakes, and L-handle brakes. FATH T-slotted hardware components are easy to install, allow for numerous T-slotted structure configurations, and have a 1-year warranty against defects.
Learn more.
Weird stuff: Moon dust simulant for 3D printing
 Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Learn more.
Break the mold with custom injection molding by Rogan
 With 90 years of industry experience, Rogan Corporation possesses the expertise to deliver custom injection molding solutions that set businesses apart. As a low-cost, high-volume solution, injection molding is the most widely used plastics manufacturing process. Rogan processes include single-shot, two-shot, overmolding, and assembly. Elevate your parts with secondary operations: drilling and tapping, hot stamping, special finishes, punch press, gluing, painting, and more.
With 90 years of industry experience, Rogan Corporation possesses the expertise to deliver custom injection molding solutions that set businesses apart. As a low-cost, high-volume solution, injection molding is the most widely used plastics manufacturing process. Rogan processes include single-shot, two-shot, overmolding, and assembly. Elevate your parts with secondary operations: drilling and tapping, hot stamping, special finishes, punch press, gluing, painting, and more.
Learn more.
World's first current-carrying fastening technology
 PEM® eConnect™ current-carrying pins from Penn-Engineering provide superior electrical connections in applications that demand high performance from internal components, such as automotive electronics. This first-to-market tech provides repeatable, consistent electrical joints and superior installation unmatched by traditional fastening methods. Features include quick and secure automated installation, no hot spots or poor conductivity, and captivation options that include self-clinching and broaching styles.
PEM® eConnect™ current-carrying pins from Penn-Engineering provide superior electrical connections in applications that demand high performance from internal components, such as automotive electronics. This first-to-market tech provides repeatable, consistent electrical joints and superior installation unmatched by traditional fastening methods. Features include quick and secure automated installation, no hot spots or poor conductivity, and captivation options that include self-clinching and broaching styles.
Learn more about eConnect pins.
New interactive digital catalog from EXAIR
 EXAIR's latest catalog offers readers an incredible source of innovative solutions for common industrial problems like conveying, cooling, cleaning, blowoff, drying, coating, and static buildup. This fully digital and interactive version of Catalog 35 is designed for easy browsing and added accessibility. Customers can view, download, print, and save either the full catalog or specific pages and sections. EXAIR products are designed to conserve compressed air and increase personnel safety in the process. Loaded with useful information.
EXAIR's latest catalog offers readers an incredible source of innovative solutions for common industrial problems like conveying, cooling, cleaning, blowoff, drying, coating, and static buildup. This fully digital and interactive version of Catalog 35 is designed for easy browsing and added accessibility. Customers can view, download, print, and save either the full catalog or specific pages and sections. EXAIR products are designed to conserve compressed air and increase personnel safety in the process. Loaded with useful information.
Check out EXAIR's online catalog.
5 cost-saving design tips for CNC machining
 Make sure your parts meet expectations the first time around. Xometry's director of application engineering, Greg Paulsen, presents five expert tips for cutting costs when designing custom CNC machined parts. This video covers corners and radii, designing for deep pockets, thread depths, thin walls, and more. Always excellent info from Paulsen at Xometry.
Make sure your parts meet expectations the first time around. Xometry's director of application engineering, Greg Paulsen, presents five expert tips for cutting costs when designing custom CNC machined parts. This video covers corners and radii, designing for deep pockets, thread depths, thin walls, and more. Always excellent info from Paulsen at Xometry.
View the video.
What can you secure with a retaining ring? 20 examples
 From the watch dial on your wrist to a wind turbine, no application is too small or too big for a Smalley retaining ring to secure. Light to heavy-duty loads? Carbon steel to exotic materials? No problem. See how retaining rings are used in slip clutches, bike locks, hip replacements, and even the Louvre Pyramid.
From the watch dial on your wrist to a wind turbine, no application is too small or too big for a Smalley retaining ring to secure. Light to heavy-duty loads? Carbon steel to exotic materials? No problem. See how retaining rings are used in slip clutches, bike locks, hip replacements, and even the Louvre Pyramid.
See the Smalley design applications.
Load fasteners with integrated RFID
 A crane, rope, or chain may be required when something needs lifting -- plus anchoring points on the load. JW Winco offers a wide range of solutions to fasten the load securely, including: lifting eye bolts and rings (with or without rotation), eye rings with ball bearings, threaded lifting pins, shackles, lifting points for welding, and more. Some, such as the GN 581 Safety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts, even have integrated RFID tags to clearly identify specific lifting points during wear and safety inspections and manage them digitally and without system interruption.
A crane, rope, or chain may be required when something needs lifting -- plus anchoring points on the load. JW Winco offers a wide range of solutions to fasten the load securely, including: lifting eye bolts and rings (with or without rotation), eye rings with ball bearings, threaded lifting pins, shackles, lifting points for welding, and more. Some, such as the GN 581 Safety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts, even have integrated RFID tags to clearly identify specific lifting points during wear and safety inspections and manage them digitally and without system interruption.
Learn more.
Couplings solve misalignments more precisely with targeted center designs
 ALS Couplings from Miki Pulley feature a simplistic, three-piece construction and are available in three different types for more precisely handling parallel, angular, or axial misalignment applications. The key feature of this coupling design is its center element. Each of the three models has a center member that has a unique and durable material and shape. Also called a "spider," the center is designed to address and resolve the type of misalignment targeted. Ideal for unidirectional continuous movement or rapid bidirectional motion.
ALS Couplings from Miki Pulley feature a simplistic, three-piece construction and are available in three different types for more precisely handling parallel, angular, or axial misalignment applications. The key feature of this coupling design is its center element. Each of the three models has a center member that has a unique and durable material and shape. Also called a "spider," the center is designed to address and resolve the type of misalignment targeted. Ideal for unidirectional continuous movement or rapid bidirectional motion.
Learn more.
What is 3D-MID? Molded parts with integrated electronics from HARTING
 3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
View the video.
Carbon nanotube 'stitches' strengthen composites, could make airplane frames lighter and more damage resistant

MIT aerospace engineers have found a new way to bond composite layers, producing a material that is substantially stronger and more resistant to damage than other advanced composites. The improvement may lead to stronger, lighter airplane parts. [Illustration: Christine Daniloff/MIT]
By Jennifer Chu, MIT
The newest Airbus and Boeing passenger jets flying today are made primarily from advanced composite materials such as carbon-fiber-reinforced plastic -- extremely light, durable materials that reduce the overall weight of the plane by as much as 20 percent compared to aluminum-bodied planes. Such lightweight airframes translate directly to fuel savings, which is a major point in advanced composites' favor.
But composite materials are also surprisingly vulnerable: While aluminum can withstand relatively large impacts before cracking, the many layers in composites can break apart due to relatively small impacts -- a drawback that is considered the material's Achilles' heel.
Now MIT aerospace engineers have found a way to bond composite layers in such a way that the resulting material is substantially stronger and more resistant to damage than other advanced composites. Their results are published in the August issue of the journal Composites Science and Technology.
The researchers fastened the layers of composite materials together using carbon nanotubes -- atom-thin rolls of carbon that, despite their microscopic stature, are incredibly strong. They embedded tiny "forests" of carbon nanotubes within a glue-like polymer matrix, then pressed the matrix between layers of carbon-fiber composites. The nanotubes, resembling tiny, vertically aligned stitches, worked themselves within the crevices of each composite layer, serving as a scaffold to hold the layers together.
In experiments to test the material's strength, the team found that, compared with existing composite materials, the stitched composites were 30 percent stronger, withstanding greater forces before breaking apart.
Roberto Guzman, who led the work as an MIT postdoc in the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AeroAstro), says the improvement may lead to stronger, lighter airplane parts -- particularly those that require nails or bolts, which can crack conventional composites.
"More work needs to be done, but we are really positive that this will lead to stronger, lighter planes," says Guzman, who is now a researcher at the IMDEA Materials Institute in Spain. "That means a lot of fuel saved, which is great for the environment and for our pockets."
The study's co-authors include AeroAstro professor Brian Wardle and researchers from the Swedish aerospace and defense company Saab AB.

The researchers' technique integrates a scaffold of carbon nanotubes within a polymer glue, which through a repetitive process becomes a stack of 16 composite plies, with carbon nanotubes glued between each layer. [Courtesy of the researchers]
"Size matters"
Today's composite materials are composed of layers, or plies, of horizontal carbon fibers, held together by a polymer glue, which Wardle describes as "a very, very weak, problematic area." Attempts to strengthen this glue region include Z-pinning and 3D weaving -- methods that involve pinning or weaving bundles of carbon fibers through composite layers, similar to pushing nails through plywood or thread through fabric.
"A stitch or nail is thousands of times bigger than carbon fibers," Wardle says. "So when you drive them through the composite, you break thousands of carbon fibers and damage the composite."
Carbon nanotubes, by contrast, are about 10 nanometers in diameter -- nearly a million times smaller than the carbon fibers.
"Size matters, because we're able to put these nanotubes in without disturbing the larger carbon fibers, and that's what maintains the composite's strength," Wardle says. "What helps us enhance strength is that carbon nanotubes have 1,000 times more surface area than carbon fibers, which lets them bond better with the polymer matrix."
Stacking up the competition
Guzman and Wardle came up with a technique to integrate a scaffold of carbon nanotubes within the polymer glue. They first grew a forest of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes, following a procedure that Wardle's group previously developed. They then transferred the forest onto a sticky, uncured composite layer and repeated the process to generate a stack of 16 composite plies -- a typical composite laminate makeup -- with carbon nanotubes glued between each layer.
To test the material's strength, the team performed a tension-bearing test -- a standard test used to size aerospace parts -- where the researchers put a bolt through a hole in the composite, then ripped it out. While existing composites typically break under such tension, the team found the stitched composites were stronger, able to withstand 30 percent more force before cracking.
The researchers also performed an open-hole compression test, applying force to squeeze the bolt hole shut. In that case, the stitched composite withstood 14 percent more force before breaking, compared to existing composites.
"The strength enhancements suggest this material will be more resistant to any type of damaging events or features," Wardle says. "And since the majority of the newest planes are more than 50 percent composite by weight, improving these state-of-the art composites has very positive implications for aircraft structural performance."
Stephen Tsai, emeritus professor of aeronautics and astronautics at Stanford University, says advanced composites are unmatched in their ability to reduce fuel costs, and therefore, airplane emissions.
"With their intrinsically light weight, there is nothing on the horizon that can compete with composite materials to reduce pollution for commercial and military aircraft," says Tsai, who did not contribute to the study. But he says the aerospace industry has refrained from wider use of these materials, primarily because of a "lack of confidence in [the materials'] damage tolerance. The work by Professor Wardle addresses directly how damage tolerance can be improved, and thus how higher utilization of the intrinsically unmatched performance of composite materials can be realized."
This work was supported by Airbus Group, Boeing, Embraer, Lockheed Martin, Saab AB, Spirit AeroSystems Inc., Textron Systems, ANSYS, Hexcel, and TohoTenax through MIT's Nano-Engineered Composite aerospace STructures (NECST) Consortium, and, in part, by the U.S. Army.
Published August 2016
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy


